跳至內容
瑜珈哲學簡介:了解基礎知識
瑜珈哲學簡介:了解基礎知識
瑜珈通常與身體姿勢和靈活性有關,但其根源更深。從本質上講,瑜珈是一種涵蓋整體生活方式的哲學,融合了思想、身體和精神。了解瑜珈哲學的基本原理可以豐富您的練習,並為您提供更平衡、更有意義的生活的見解。讓我們探討這些基礎概念及其與現代生活的相關性。
1. 瑜珈哲學的精髓
瑜伽哲學植根於古代經典,例如帕坦伽利的《瑜伽經》、《薄伽梵歌》和《奧義書》。這些文本概述了指導個人實現自我實現和內心平靜的原則和實踐。
-
結合: 「瑜珈」這個字本身就是結合的意思。它像徵著身體、心靈和精神的融合,旨在協調這些方面以達到平衡和寧靜的狀態。
-
自我實現: 瑜珈哲學鼓勵自我探索和理解超越自我或身體身分的真實本質。
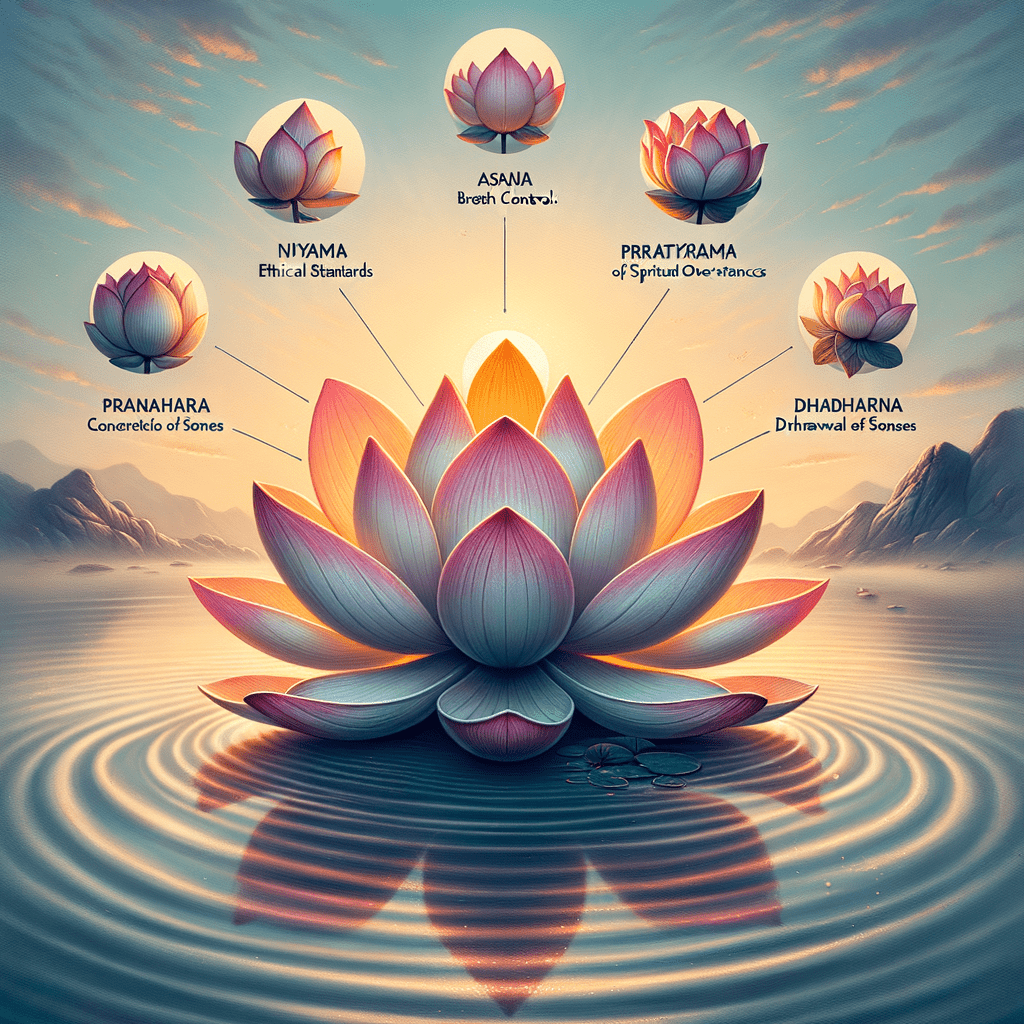
2. 瑜珈八支
帕坦伽利的《瑜伽經》中描述了瑜伽的八支,為個人發展和精神成長提供了一個全面的框架:
-
Yamas(道德準則): 指導與他人互動的道德原則,包括非暴力(Ahimsa)和誠實(Satya)。
-
Niyamas(個人遵守): 培養紀律和內心平靜的做法,例如滿足(Santosha)和自學(Svadhyaya)。
-
體位法(Asana,身體姿勢): 練習身體姿勢,為冥想做好準備。
-
調息(呼吸控制): 調節呼吸以增強能量流動和頭腦清晰度的技巧。
-
制感(感官撤退): 透過將注意力從外在幹擾中撤出而轉向內心。
-
專注 (Dharana): 將思想集中在一個點或物體上。
-
禪定(冥想): 持續的專注,從而達到冥想狀態。
-
三摩地(啟蒙): 冥想意識與與神合一的終極狀態。
3. 身心靈的聯繫
瑜珈哲學強調心靈、身體和精神的相互連結:
-
心靈: 透過冥想和正念等練習,瑜珈有助於平靜心靈、減輕壓力並增強思考清晰度。
-
身體: 身體姿勢(體位法)可以增強和平衡身體,促進健康和活力。
-
精神: 瑜珈中的精神練習可以培養人與自己和宇宙之間更深層的聯繫,從而產生一種目標感和成就感。
4. 與現代生活的關聯
在當今快節奏的世界裡,瑜珈哲學為應對生活中的挑戰提供了寶貴的工具:
-
減輕壓力: 正念練習透過促進放鬆和存在感來幫助管理壓力。
-
情緒韌性: 道德準則培養同情心和同理心,增強與他人的關係。
-
個人成長: 自我反省鼓勵持續學習和個人發展。
結論
了解瑜珈哲學的基礎知識可以透過促進思想、身體和精神之間的和諧來改變您的生活方式。當你探索這些原則時,請記住瑜珈是一次個人旅程——以好奇心和開放的心態擁抱它。透過將這些教導融入您的日常生活,您可以在生活的各個方面培養更高的意識、平衡和滿足感。無論您是瑜珈新手還是正在深入練習,這些基礎概念都為成長和轉變提供了堅實的基礎。
- 選擇項目後,整個頁面將重新整理。
- 在新視窗中開啟。